The National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) has issued a notice which states that UPI, IPMS, and other payment systems of specific banks across India will be temporarily unavailable to customers. This disruption is caused due to a ransomware attack on the systems of C-Edge Technologies, which provides services for multiple banks across the country. According to the C-Edge Technologies official website, the company is a joint venture between Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) and the State Bank of India (SBI).
The ransomware attack on C-Edge Technologies service provider has made the shutdown of payment systems across nearly 300 small local banks in India. To prevent any further damage, these small banks have been isolated from the broader national payment network of India. This has caused, all online transactions, including RTGS and UPI payments, get affected. This event has led to instances where money is deducted from the sender’s account but not credited to the receiver’s account.
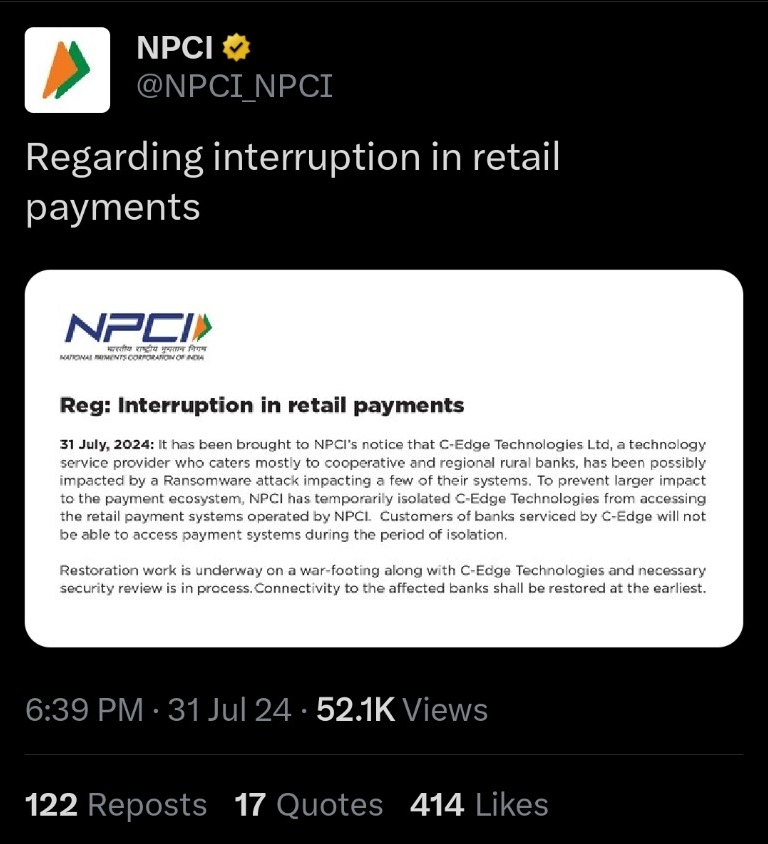
Although this ransomware attack affected mostly smaller banks, it impacts only about 0.5% of the country’s total payment system volumes. All over India, there are nearly 1,500 cooperative and regional banks, which are primarily operating outside major cities. These are the ones impacted by this incident.
What is a Ransomware Attack?
A ransomware attack is a malicious software, or malware, that encrypts a victim’s data or locks them out of their systems. Then a ransom payment is demanded by the attackers in exchange for restoring access to the data or systems.
Some ransomware attacks use more sophisticated methods like double and triple extortion. In double extortion, attackers threaten the victim to release their stolen data if the ransom is not paid, while in triple extortion, the attackers use the stolen data to target the victim’s customers or partners.
How is it sent to the victim?
Ransomware can be sent through various methods, which includes pushing emails, malicious websites, or through various loop-holes in software. According to the CERT-IN Ransomware report conducted in 2022, there was a 53% increase in ransomware incidents reported compared to the previous year.
The main sectors which were mostly got impacted were the IT sectors, followed by finance and manufacturing. Ransomware attackers have targeted critical infrastructure organizations and disrupted essential services to pressure and extract ransom payments.
The report has also stated that in the Indian context, the most frequently used malware software is the Lockbit ransomware variant, followed by Makop and DJVU/Stop ransomware. Many other new variants were also detected in 2022, including Vice Society and BlueSky. The leaking of ransomware source codes has led to the creation of new ransomware brands which has complicated the cybersecurity landscape.
The impact of such ransomware attacks extends beyond the immediate disruption of services. They possess a significant threat to the stability and security of the financial system of a country, particularly for smaller banks with limited resources to defend against such sophisticated cyberattacks.
The temporary unavailability of a robust payment systems underscores the importance of strict cybersecurity measures and the need for continuous vigilance and improvement in defending against such threats.
As the banking sector deals with this latest ransomware attack, it is also a reminder of the vulnerabilities that inherent in the digital infrastructure on which modern financial transactions depends on. It is a preventive measure to contain the spread of the ransomware and remove further damage by isolating nearly 300 small banks from the country’s payment network. However, it also highlights the inter connection of financial systems and the potential for widespread disruption when a single service provider is compromised.
In conclusion, the ransomware attack on C-Edge Technologies and the subsequent shutdown of payment systems in numerous small banks can be seen as a critical warning about the persistent threat of cyberattacks. The financial sector, particularly smaller banks, must prioritize cybersecurity to safeguard their systems and protect their customers from the fallout of such attacks. The CERT-IN report’s findings on the rise of ransomware incidents and the emergence of new variants underscore the need for continued vigilance and adaptation in cybersecurity strategies to counter the evolving threats in the digital age.
To read more topics, please visit: https://insightfulbharat.com

